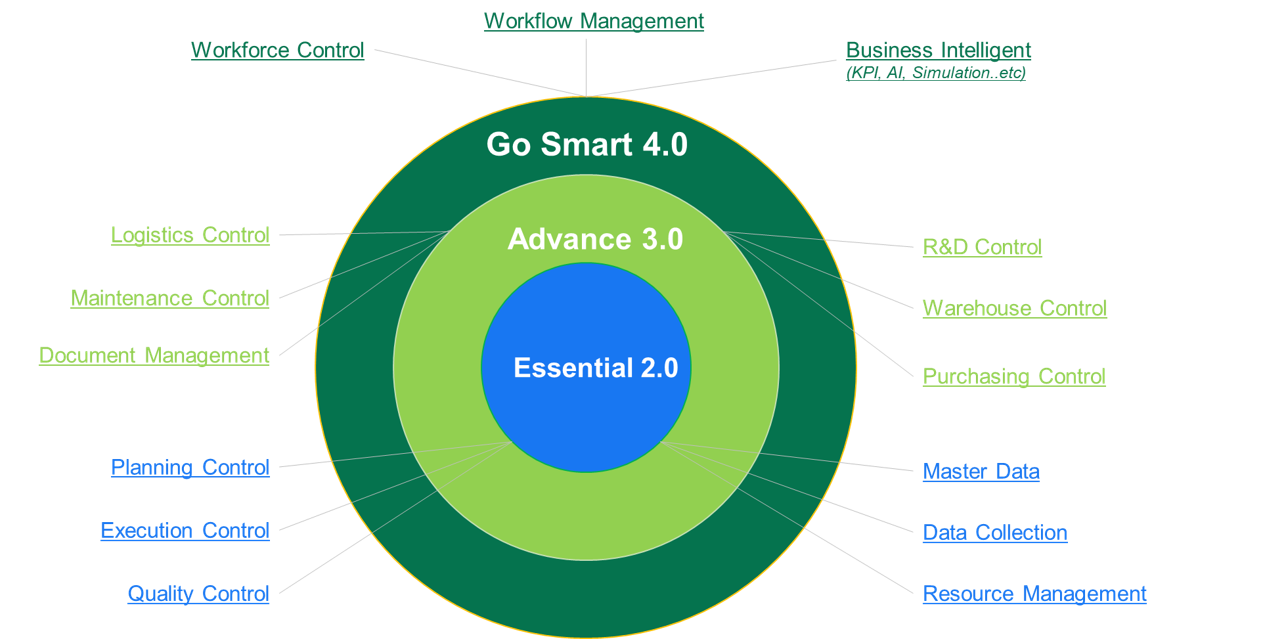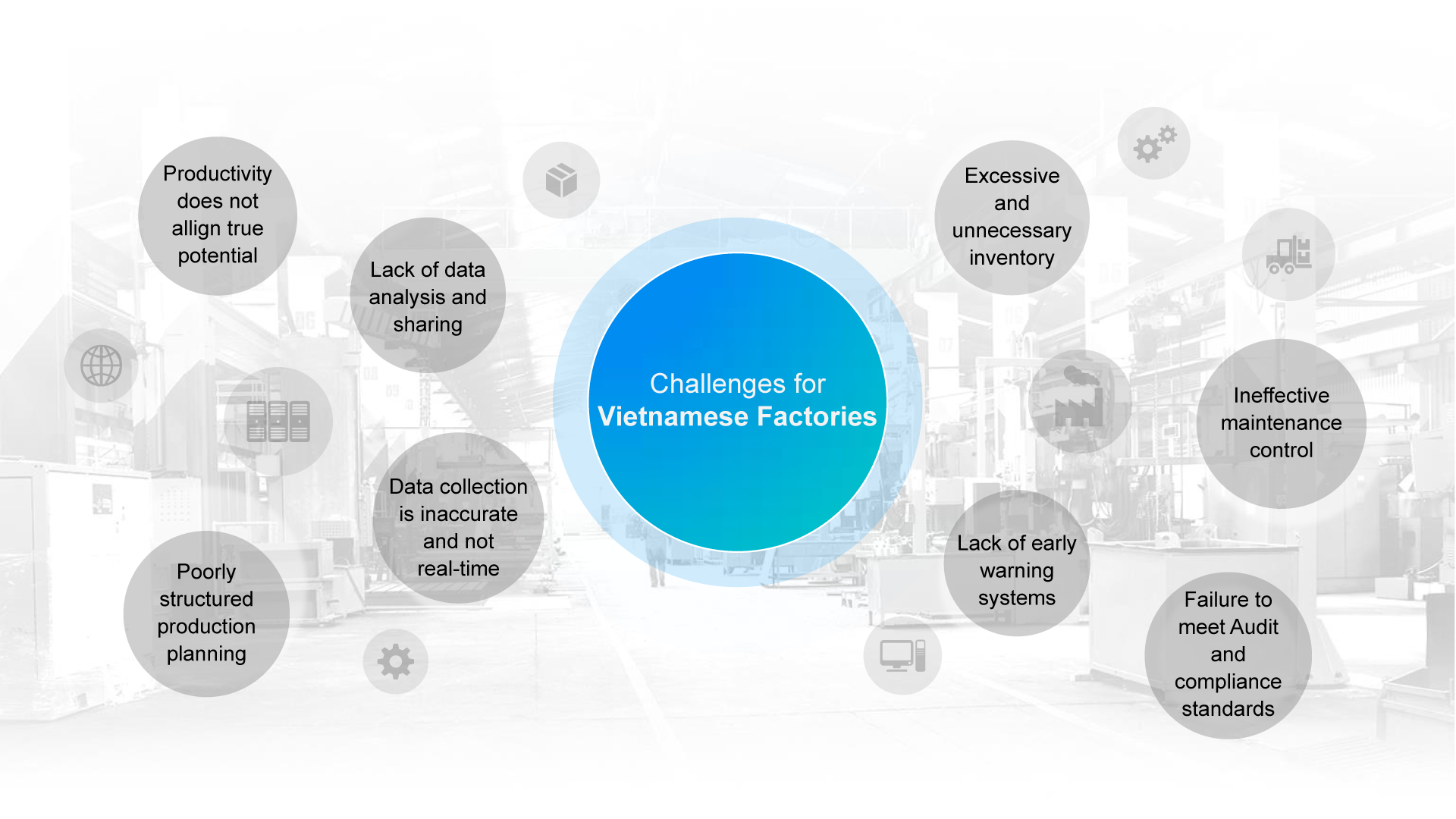
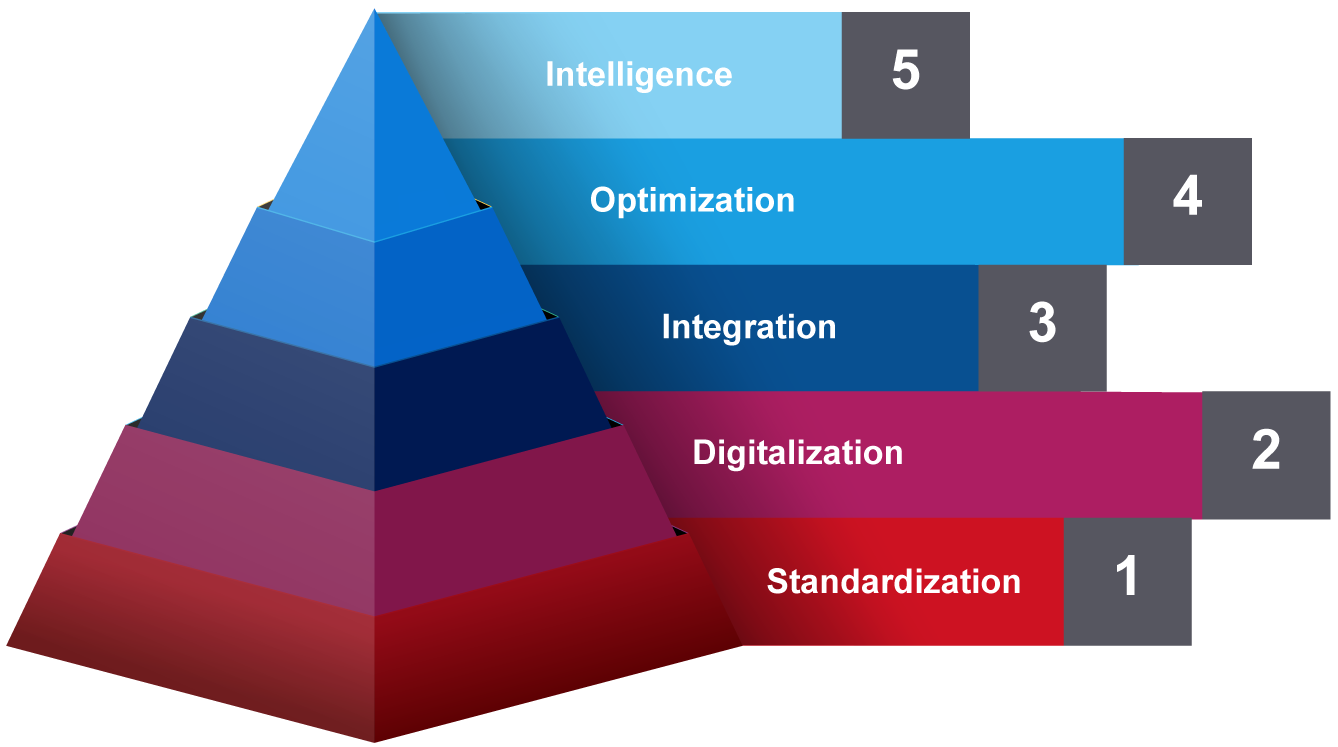
A continuous process
of transforming events into data
to optimize resources.
The Role of ControlMES Manufacturing Execution System
Capture real-time shop-floor data, turn it into clear, actionable insights, and enable managers to make smart, timely decisions — driving faster and higher-quality production.
- counter_1Connect & remotely control equipments.
- counter_2Collect real-time production data.
- counter_3Production visualization.
- counter_4Analyze & predict (early detection).
- counter_5Optimize manufacturing operations.
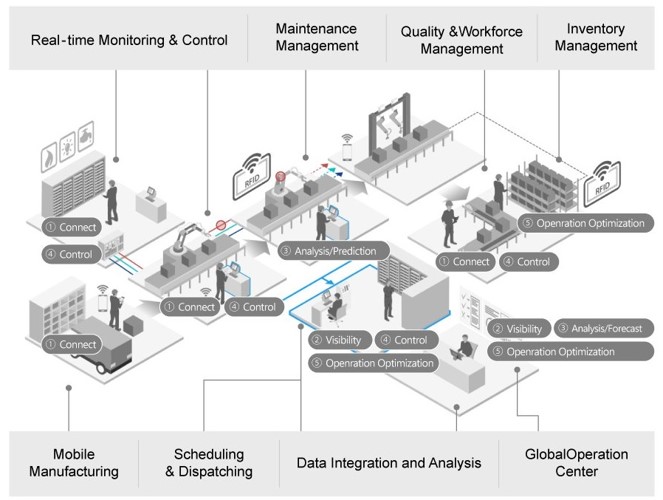
01. Production Planning & Scheduling
Go beyond simple scheduling — deeply optimize production reality to minimize waste, boost throughput, and secure on-time delivery, a critical success factor in manufacturing.
- circle Plan by customer orders and product specifications.
- circle Multi-step planning across production lines.
- circle Optimize production schedules to reduce waste.
- circle Detailed material planning for each production step.
- circle Rapid rescheduling in case of incidents or changes.
- circle Performance analytics on planning effectiveness.
- circle Integration with ERP and warehouse systems.
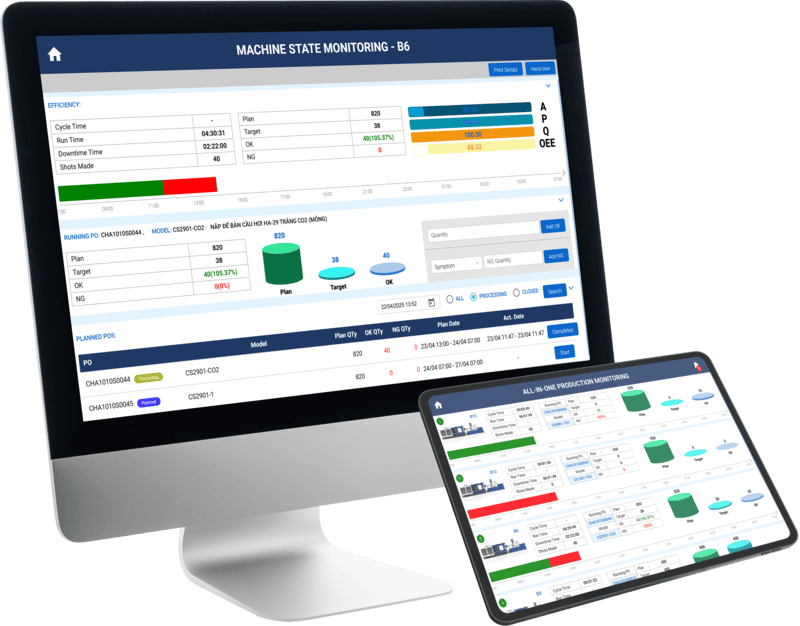
02. Real-Time Production Monitoring
The core of ControlMES: reflect live shop-floor status so managers instantly know what is happening in the factory.
- circle Track order progress in real time.
- circle Monitor machine and line status.
- circle Monitor production performance (OEE).
- circle Real-time dashboard and shop-floor display screens.
- circle Log downtime causes, delays, and quality issues.
- circle Track actual material consumption.
- circle Instant reports and live charts.
03. Comprehensive Quality Management
Enforce standard operating procedures, monitor product quality metrics, and trigger corrective actions immediately when deviations occur.
- circle Define quality standards.
- circle Perform IQC, in-process (PQC), and OQC inspections.
- circle Manage defects and perform root-cause analysis.
- circle Manage rework processes.
- circle Link production data for full traceability.
- circle Perform statistical quality analysis.
- circle Generate comprehensive quality reports.
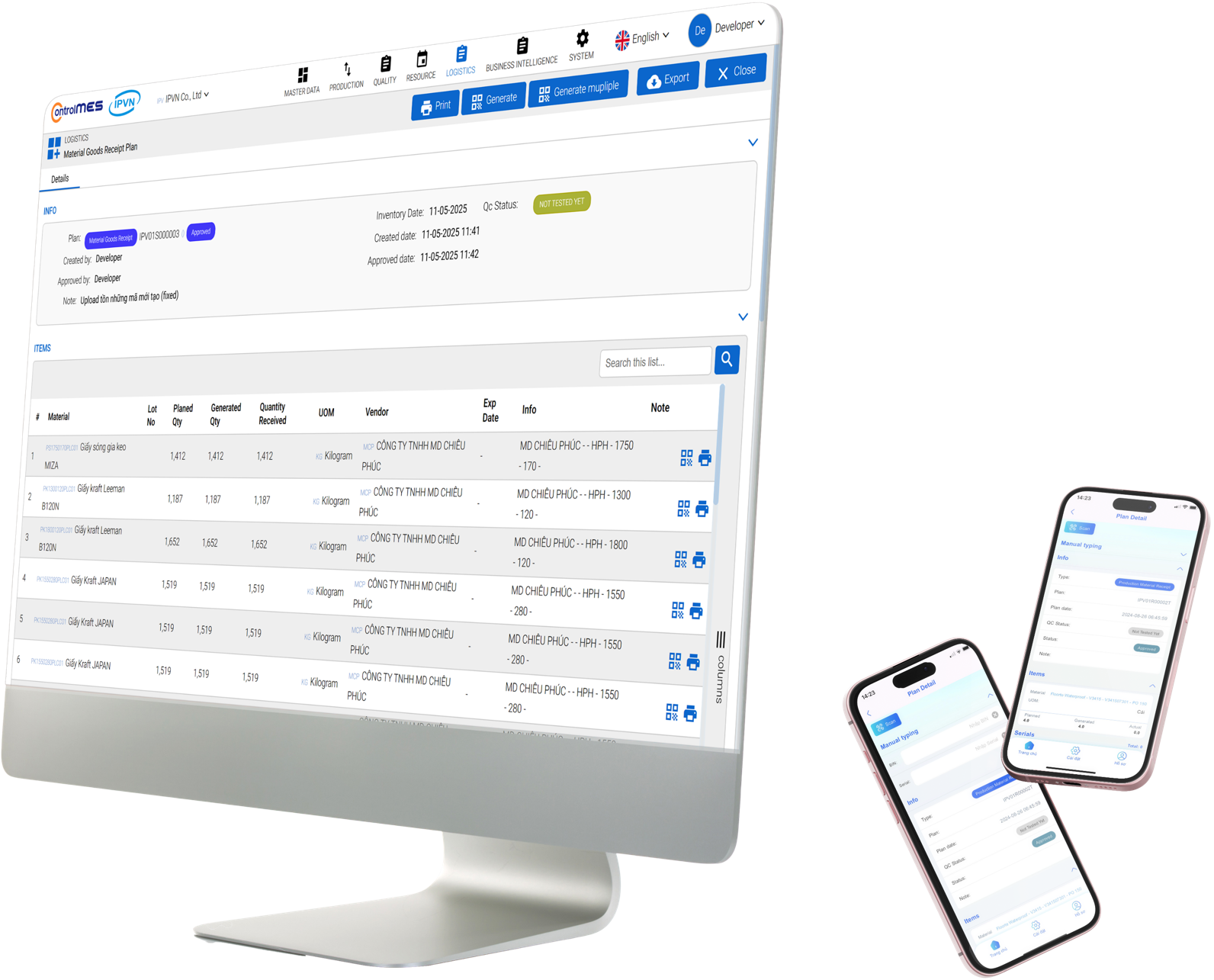
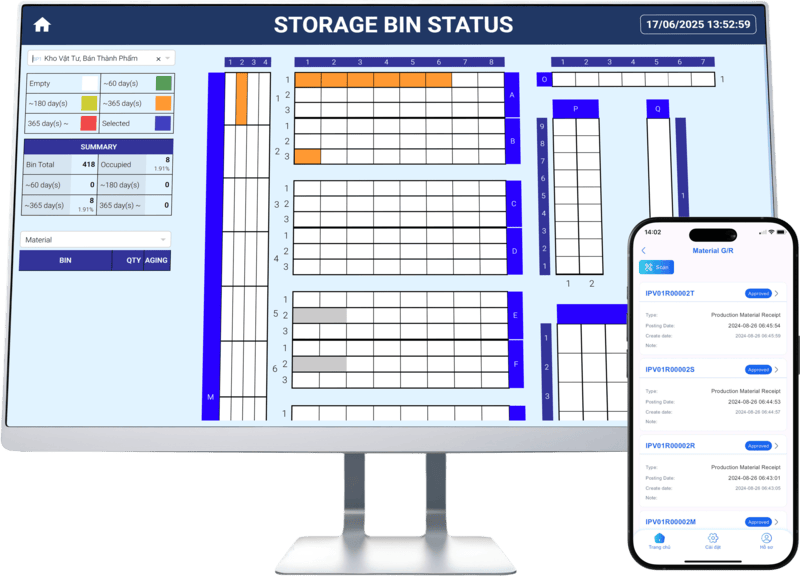
04. Material Flow Management
The crucial bridge between warehouse, production, and quality — ensuring materials are always available, at the right place, right time, and right specification.
- circle Receive and allocate materials.
- circle Track material movement across the shop floor.
- circle Manage material usage by production step.
- circle Automatically calculate consumption and detect variances.
- circle Integrate with scales, sensors, and label printers.
- circle Manage reverse material flow (scrap, re-use).
- circle Enable traceability integration.
- circle Connect to ERP and central warehouse systems.
05. Equipment Maintenance Management
Transform from reactive to proactive maintenance, and from time-based to condition-based strategies — maximizing equipment uptime and extending asset life.
- circle Manage equipment inventory and hierarchy.
- circle Plan and schedule preventive maintenance.
- circle Track unplanned maintenance and breakdowns.
- circle Enable condition-based maintenance.
- circle Manage maintenance requests and work orders.
- circle Track spare parts and consumables.
- circle Maintain equipment and maintenance history.
- circle Generate maintenance performance analytics.
- circle Role-based access and electronic sign-off.
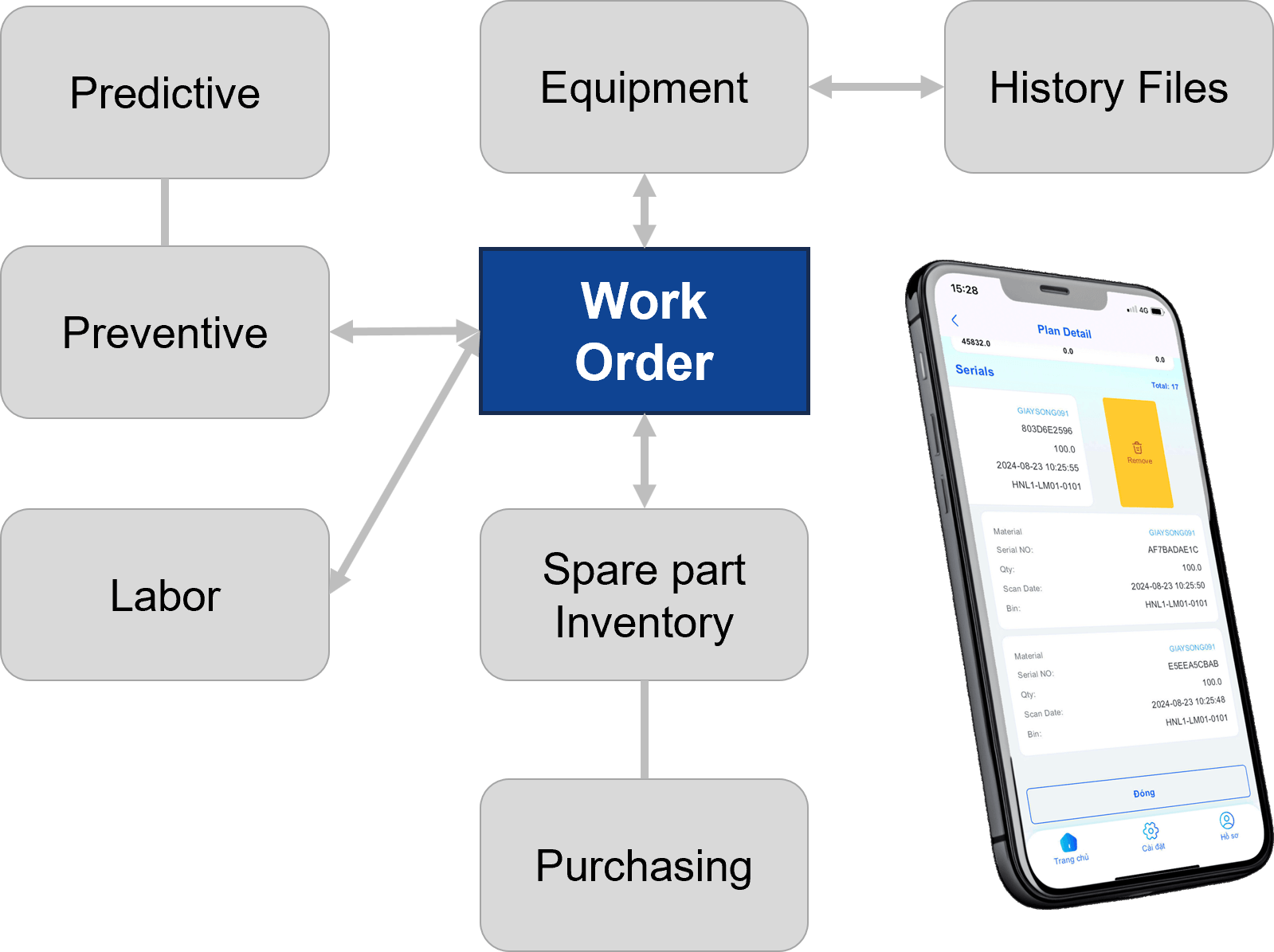
06. Factory Resource Management
Ensure optimal allocation of human resources, machines, tools, molds, and fixtures — reducing downtime and maximizing overall plant productivity.
- circle Manage production workforce.
- circle Monitor machine and equipment availability.
- circle Plan and allocate resources efficiently.
- circle Manage tools, molds, and jigs.
- circle Measure resource utilization and performance.
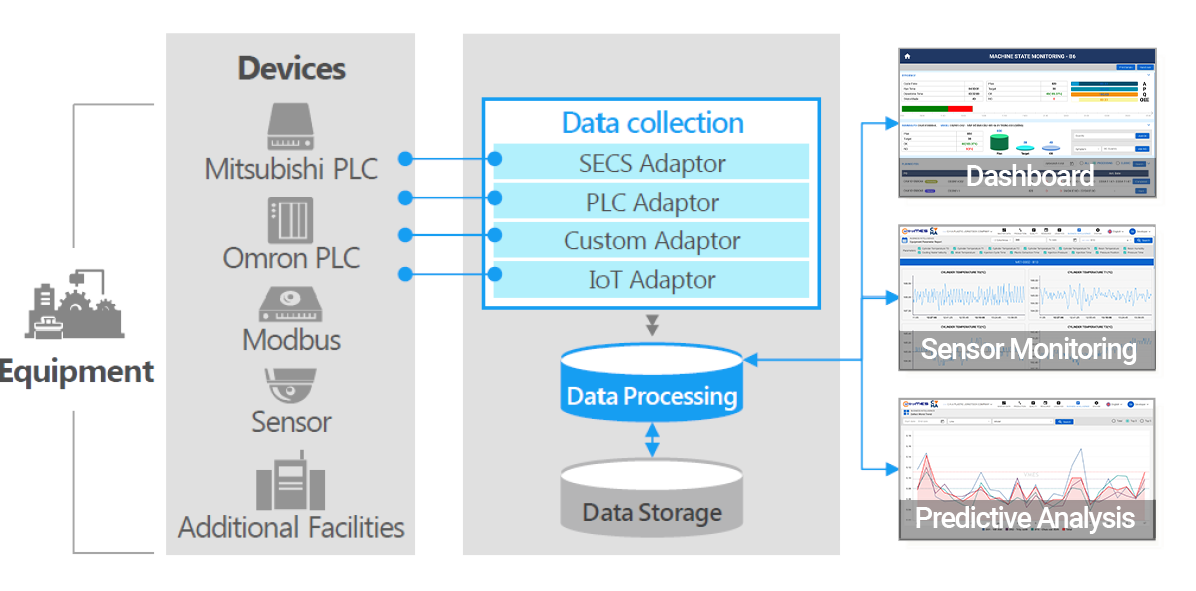
07. Machine Connectivity
The bridge between the physical world (machines, sensors, devices) and digital management — enabling automation, real-time monitoring, and true smart manufacturing.
- circle Communicate with machines via OPC UA, Modbus TCP/RTU, MTConnect, Siemens S7, EtherNet/IP, etc.
- circle Collect production data in real time.
- circle Analyze equipment status (OEE, downtime, anomalies).
- circle Connect to auxiliary devices.
- circle Generate automatic alerts & equipment logs.
- circle Integrate with SCADA, IoT, and cloud platforms.
08. Master Data Management
The single source of truth for synchronized, accurate production data — powering planning, operations, monitoring, reporting, and analytics across ControlMES.
- circle Products.
- circle Processes & operations.
- circle Machines & equipment.
- circle Materials.
- circle BOM and BOM levels.
- circle Personnel & roles.
- circle Quality parameters.
- circle Shift patterns and holidays.
- circle Defect symptoms & Defect causes.
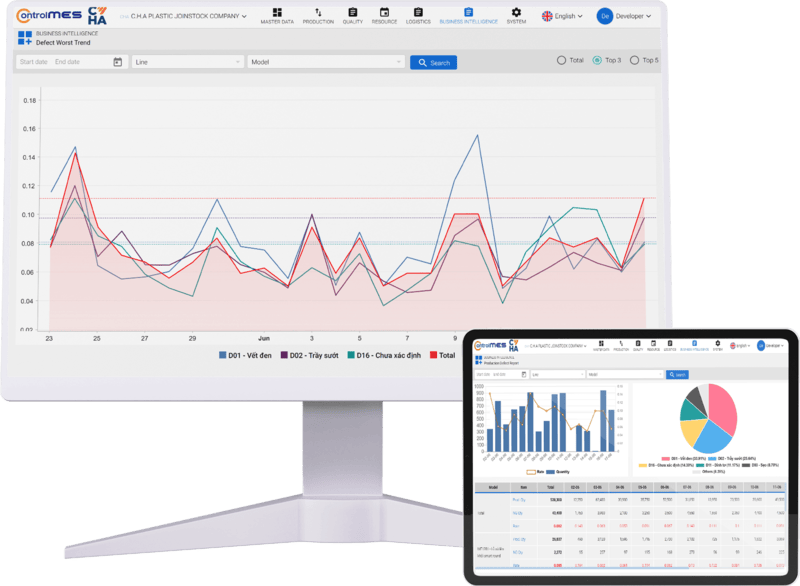
09. Reporting & Analytics
The “brain” of ControlMES — turning real-time production data into clear, actionable insights. Get a bird’s-eye view of the entire factory while drilling into every bottleneck in detail.
- circle Historical reports & trend analysis.
- circle Proactive & smart alerts.
- circle Root-cause analysis.
- circle Customizable reports & data filters.
- circle Integration with BI or ERP systems.
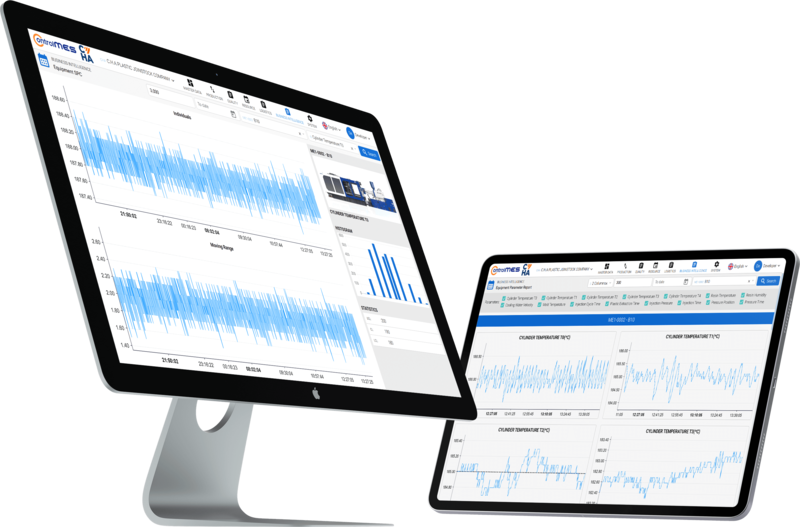
- counter_1 Increasing production complexity?
- counter_2 Demand for real-time data?
- counter_3 Need for consistent product quality?
- counter_4 Planning to scale production?
- counter_5 Compliance and audit pressure?
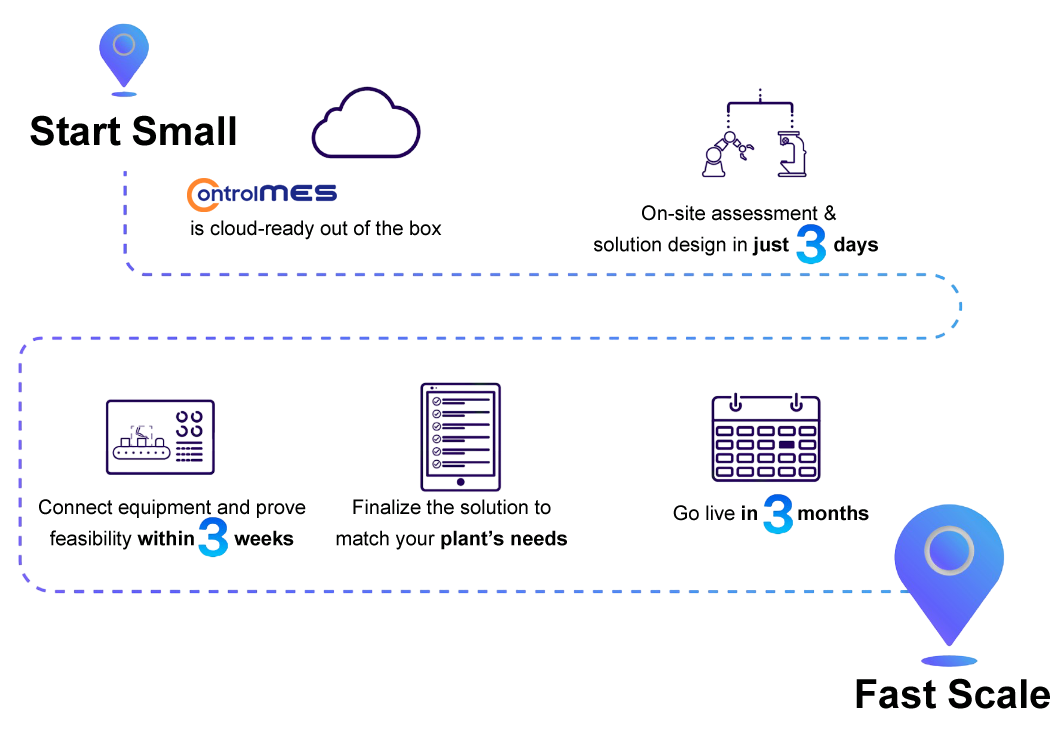
Upgrade & Expand
With an open and modular design, the system is built to support all future upgrades and expansions according to each factory’s unique needs.